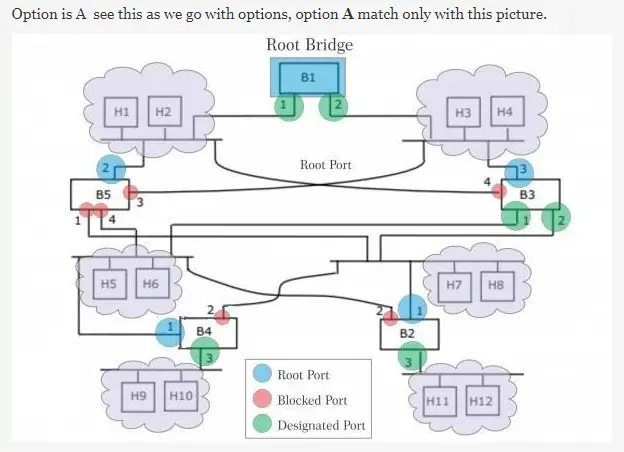
Q. 27 Consider the diagram shown below where a number of LANs are connected by (transparent) bridges. In order to avoid packets looping through circuits in the graph, the bridges organize themselves in a spanning tree. First, the root bridge is identified as the bridge with the least serial number. Next, the root sends out (one or more) data units to enable the setting up of the spanning tree of shortest paths from the root bridge to each bridge. Each bridge identifies a port (the root port) through which it will forward frames to the root bridge. Port conflicts are always resolved in favour of the port with the lower index value. When there is a possibility of multiple bridges forwarding to the same LAN (but not through the root port), ties are broken as follows: bridges closest to the root get preference and between such bridges, the one with the lowest serial number is preferred. 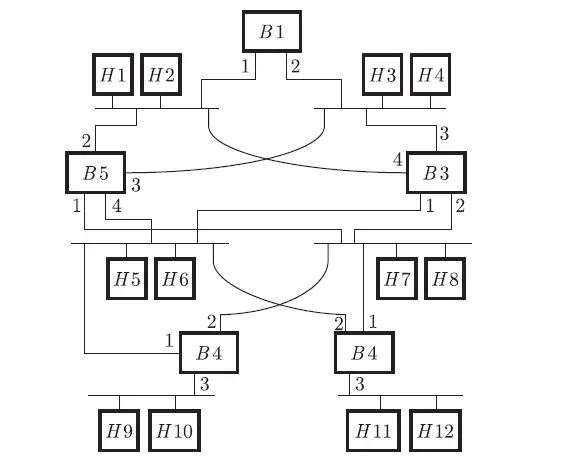
(A)
| Hosts | Port |
| H1, H2, H3, H4 | 3 |
| H5, H6, H9, H10 | 1 |
| H7, H8, H11, H12 | 2 |
(B)
| Hosts | Port |
| H1, H2 | 4 |
| H3, H4 | 3 |
| H5, H6 | 1 |
| H7, H8, H9, H10,H11,H12 | 2 |
(C)
| Hosts | Port |
| H3, H4 | 3 |
| H5, H6, H9, H10 | 1 |
| H1, H2 | 4 |
| H7, H8, H11, H12 | 2 |
(D)
| Hosts | Port |
| H1, H2, H3, H4 | 3 |
| H5, H7, H9, H10 | 1 |
| H7, H8, H11, H12 | 4 |
Answer: (A)
Explanation: