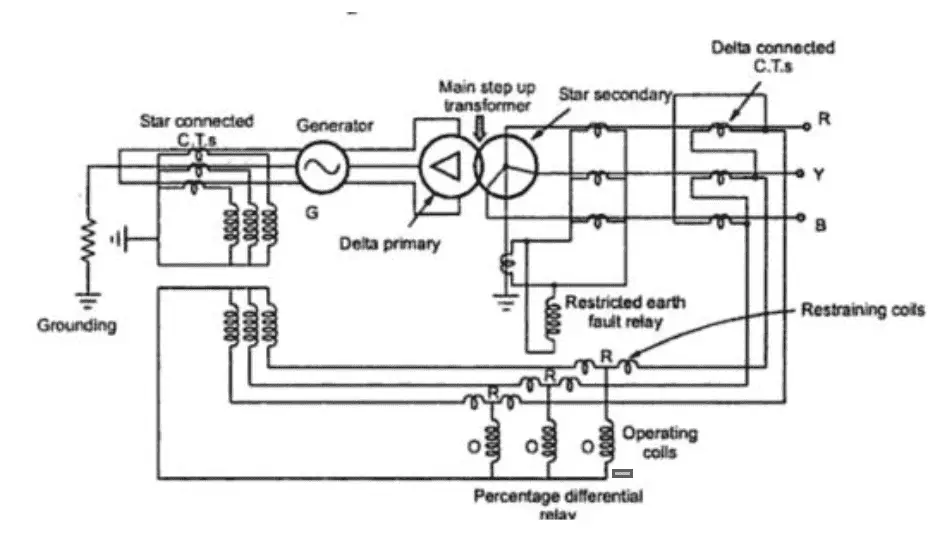
Generator and Transformer Unit Biased Differential Protection:
In a high voltage transmission system, the bus bars are at very high voltages than the generators. The generators are directly connected to step up transformer to which it is connected, together from a generator transformer unit. The protection of such a unit is achieved by differential protection scheme using circulating current principle. While providing protection to such a unit, it is necessary to consider the phase shift and current transformation in the step up transformer.
[wp_ad_camp_1]
The figure in the following page, shows a biased differential protection scheme used for generator transformer unit. The zone of such a scheme includes the stator windings, the step up transformer and the intervening connections.
[wp_ad_camp_1]
The transformer is delta-star hence the current transformers on high voltage side are delta connected while those on generator side are star connected. This cancels the displacement between line currents introduced by the delta connected primary of the transformer. Where there is no fault, the secondary currents of the current transformer connected on generator side are equal to the currents in the pilot wires from the secondaries of the delta connected current transformers on the secondary of main transformer. When a fault occurs, the pilot wires carry the differential current to operate the percentage differential relay.
For the protection against the earth faults, an earth fault relays is put in the secondary winding of the main step up transformers as shown. In such a case, differential protection acts as a backup protection to the restricted earth fault protection. This overall differential protection scheme does not include unit transformer as a separate differential scheme is provided it.
PHASE FAULT
- Phase-phase faults clear of earth are less common. They may occur on the end portion of stator coils or in the slots if the winding involves two coil sides in the same slot. In the later case the fault will involve earth in a very short time.
- Phase fault current is not controlled by the method of earthing the neutral point.
INTERTURN FAULTS
- Interturn faults are also uncommon, but not unknown
- A greatest danger arising from failure to deal with interturn faults quickly is fire. A large portion of the insulation is inflammable






![What is Arc Chute? Types, Working Principle [Video Included] arc chute working priciple](https://www.electrical4u.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/arc-chute-218x150.png)