Loss of Field or Loss of Excitation Protection:
Loss of excitation protection is used to protect the synchronous machine (alternator or generator) acts as induction motor when the excitation fails. Loss excitation protection operates under many circumstances such as diode failure, rotor winding short circuit, AVR failure, etc.
Under normal condition the generator is connected to the grid, it generates reactive power along with active power to the grid and the rotor speed is same as that of grid frequency. Loss of field or loss of excitation results in loss of synchronism between rotor flux & stator flux (the generator still in online with the grid). The generator works as an induction motor at higher speed and draws reactive power from the grid. This will result in the flow of slip frequency currents in the rotor body as well as severe torque oscillations in the rotor shaft. As the rotor is not designed to sustain such currents or to withstand the high alternating torques which results in rotor overheating, coupling slippage and even rotor failure.
[wp_ad_camp_1]
A loss of excitation normally indicates a problem with the excitation system. Sometimes it may be due to inadvertent tripping of filed breaker, open or short circuit of field winding or loss of source to the exciter. If the generator is not disconnected immediately when it loses excitation wide spread instability may very quickly develop and major system shutdown may occur.
When loss of excitation alarm annunciates at annunciation panel, the machine may probably be running with less excitation at leading MVAR power. Increase the excitation on the machine until it reaches on lagging MVAR power. The machine trips on the same protection along with alarm resynchronize the machine and try to stabilize at required MVAR power. If not possible, trip the machine immediately and inform to the maintenance staff for thorough checking of the Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR) and its associated parts.
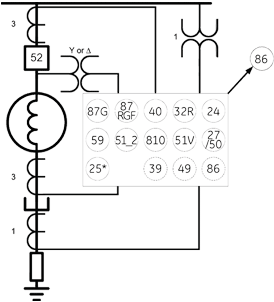
Loss of Field or Loss of Excitation Protection ANSI Code: 40
Relays acted :
- Flag operation at Protection panel.
- 86 M generator Master Trip relay Acted
[wp_ad_camp_1]
Ref: http://www.indiastudychannel.com/projects/4294-Generator-Protection-Schemes.aspx






![What is Arc Chute? Types, Working Principle [Video Included] arc chute working priciple](https://www.electrical4u.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/arc-chute-218x150.png)